Units refer to the total amount of units of output you expect from the asset (for a vehicle, you might expect to drive 100,000 miles, so you would have 100,000 total units. It is important to note that an asset’s book value does not indicate the vehicle’s market value since depreciation is merely an allocation technique. The extra amounts of depreciation include bonus depreciation and Section 179 deductions. Consequently, the net value of the van will amount to 0 at the end of its useful life in 10 years.
Depreciation in Financial Statements
Calculate the accumulated depreciation and net book value of the equipment at the end of the third year. Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a does accumulated depreciation have a credit balance Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors.

Financial Reporting
A Trial Balance of the business shows the closing balances of all the general ledgers. Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
Accumulated depreciation journal entry
Depreciation is expensing the cost of an asset that produces revenue during its useful life. Buildings, machinery, furniture, and fixtures wear out, computers and technology devices become obsolete, and they are expensed as their value approaches zero. Accumulated depreciation is the total value of the asset that is expensed. It is a Contra asset account as it reduces the balance in the asset account. If the accumulated depreciation is subtracted from the original value of the asset, the present value of the asset can be found.
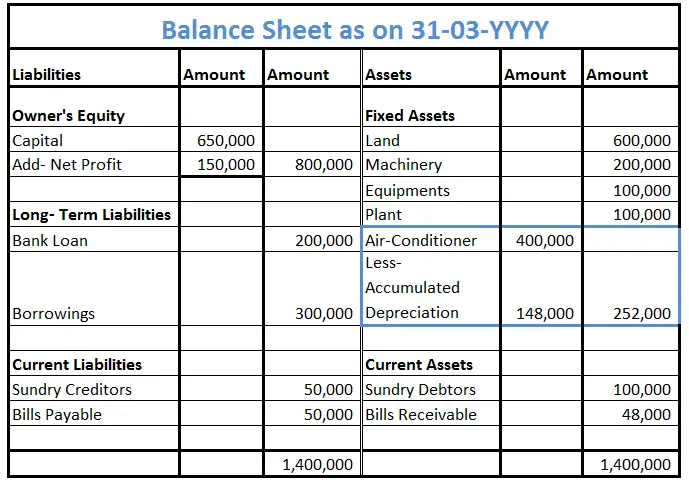
Accumulated depreciation represents the total depreciation of a company’s fixed assets at a specific point in time. Also, fixed assets are recorded on the balance sheet, and since accumulated depreciation affects a fixed asset’s value, it, too, is recorded on the balance sheet. When a depreciation expense is recorded, the accumulated depreciation account gets credited, which in turn increases the balance of the contra-asset account and lowers the net book value of the related asset.
Each method allocates the depreciation expense differently over the asset’s useful life. On most balance sheets, accumulated depreciation appears as a credit balance just under fixed assets. In some financial statements, the balance sheet may just show one line for accumulated depreciation on all assets.
- Instead, the balance sheet might say “Property, plant, and equipment – net,” and show the book value of the company’s assets, net of accumulated depreciation.
- For tax purposes, businesses use depreciation to reduce their taxable income.
- For each of these assets, accumulated depreciation is the total depreciation for that asset up to and including the current accounting period.
- These assets have a useful life that extends beyond one year, and their value decreases over time due to usage, wear and tear.
- The most commonly used depreciation methods include straight-line depreciation, double declining balance, and units of production.
The company estimates that the equipment has a useful life of 5 years with zero salvage value. The company’s policy in fixed asset management is to depreciate the equipment using the straight-line depreciation method. Accumulated depreciation is an account with a credit balance, known as a long-term contra-asset account, that is reported on the balance sheet as an offset to Property, Plant and Equipment. The amount of a long-term asset’s cost that has been allocated, since the asset was acquired.
When accounting for assets, the difference between the asset’s account balance and the contra account balance is referred to as the book value. There are two major methods of determining what should be booked into a contra account. This type of account could be called the allowance for doubtful accounts or a bad debt reserve. The balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts represents the dollar amount of the current accounts receivable balance that is expected to be uncollectible. The amount is reported on the balance sheet in the asset section immediately below accounts receivable.
It depreciates over 10 years, so you can take $2,500 in depreciation expense each year. Since land and buildings are bought together, you must separate the cost of the land and the cost of the building to figure depreciation on the building. Most businesses have assets that are used to create a product or service. Over the years, these assets may incur wear and tear, reducing the dollar value of those assets. The accumulated depreciation of the van will increase by $2,000 for each year of its useful life.
The new equipment’s value decreases to $900,000, or $1 million minus $100,000. Using a similar approach, the equipment’s book value is zero at the end of the tenth year. In addition to its effect on the balance sheet, depreciation has a significant impact on the income statement. The depreciation expense for a given period (quarter or year) is recognized as an expense, which in turn reduces the company’s net income.

コメント